KINEMATICS OF MACHINES 2131906 ASSIGNMENT 1 INTRODUCTION OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS 1 Distinguish between. TOM Yatin Kumar Singh Page 3 Kinematic Pairs According to the Relative Motion Sliding.
1 According to the type of relative motion between the elements.

. Four Bar Chain Or Four Bar Mechanism. Iii Nature of relative motion. Foot C pushes ball B to the left.
Types of Kinematic Pairs. What are the different types of Kinematic Chains. State at least one similarity and one difference between a helical pair and cylindrical pair.
An engineer in designing the various parts of a machine. Type of Mechanical Constraint. Ii Analysis and synthesis of mechanisms.
State and prove kennedys three centre theorem. Types of Kinematic Pairs. Types of Kinematic Pairs.
Types of relative motion Contact and Types of mechanical constraint or Type of closure. Iii Kinematics and dynamics. Iii Ball and Socket Joint Kinematic Pair can be classified into different types based on the following criteria-1Type of relative motion between the different elements of the pair.
2 Each joint or kinematic pair and its type. The term lower kinematic pair was coined by Reuleaux to describe kinematic pairs with surface contact. The contact surfaces of the two links are similar.
Iii Nature of relative motion. I Mechanism and machine. B What is the difference between a mechanism and a machine.
Kinematics is used in astrophysics to describe the motion of celestial bodies and systems. Lets discuss the Kinematic pairs in more details with the different constraints and definitions of links and the machine elements. The main practical advantage of lower kinematic pairs over higher kinematic pairs is their.
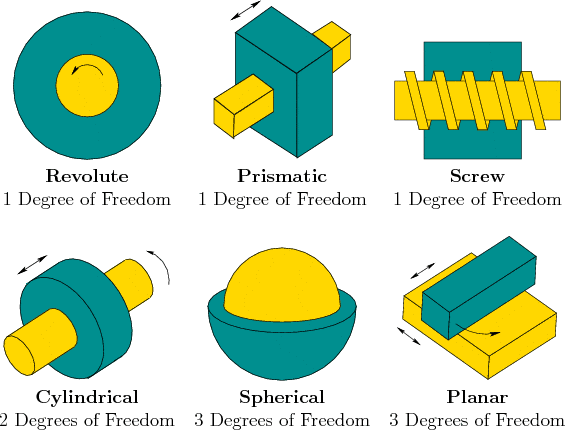
Examples of Kinematic Pairs are - i Rectangular bar in a rectangular hole. What is the difference between a higher and a lower pair. Spherical pair plane pair cylindrical pair revolute pair prismatic pair and screw pair.
Answer any three of the following. Classification of Theory of Machines as following four branches. The four Bar chain.
Figure 4-5 A spherical pair S-pair A spherical pair keeps two spherical centers together. Kinematic link kinematic pair and kinematic chain. Four Bar chain is also is known as the Quadric Cycle chain.
The second pair of action-reaction force pairs is. He used the term higher kinematic pair to describe kinematic pairs with point or curve contact. A pair of links having surface or area contact between the members is known as a lower pair.
Ii Nature of mechanical constraint. The relative motion between the two links or machine elements are completely constrained in a defined direction Then the pair is known as the Kinematic Pair. 02 Classification on any 2 basis with sub types 01 Mark each Types of Kinematic pairs.
Explain at least two pairs with neat. Kinematic pairs can be classified according to i Nature of contact. From the time of Archimedes to the Renaissance mechanisms were viewed as constructed from simple machines such as the lever pulley screw wheel and axle wedge and inclined plane.
A What is a quick return mechanism. I Nature of contact. Ii Analysis and synthesis of mechanisms.
A Lower Pair b Higher Pair 18. Explain it with a suitable diagram. C What is a kinematic pair.
ASSIGNMENT 1 INTRODUCTION OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS. The type of contact between the elements can be point P curve C or surface S. The Single Slider Crank Chain mechanism is nothing but the modified Four Bar mechanism.
Kinematic pairs can be classified according to i Nature of contact. Kinematic pairs can be classified according to. KINEMATICS PAIRS and its classification Kinematic Inversions of Four Bar Chain Slider Crank and Double Slider Crank Mechanism Introduction of Kinematics of Machines.
In Fig12 links 1 and 2 2 and 3 3 and 4 and 4 and 1 constitute kinematic pairs. And ball B pushes foot A to the left. The first pair of action-reaction force pairs is.
Kinematic link kinematic pair and kinematic chain. Reuleaux focused on bodies called links and the connections between these bodies called kinematic pairs or joints. Single Slider Crank Chain.
Foot A pushes ball B to the right. KINEMATICS OF MACHINES 2131906 ASSIGNMENT 1 INTRODUCTION OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS. Ii Nature of mechanical constraint.
Iii Nature of relative motion. A formal study of physics begins with kinematics. And ball B pushes foot C to the right.
Type of contact 3. Ii Nature of mechanical constraint. I Mechanism and machine.
Define DOF of a mechanism. The Kinematic analysis of gait using three-dimensional analysis laboratories utilizes a system of video cameras in standard fixed positions thereby capturing the movement of reflective markings attached to the skin of the individual and forwarding it to a computer to create three-dimensional movement simulations models and visualization of real movements in a. Explain at least be three features.
A kinematic schematic or diagram is drawing that clearly defines the kinematic nature of a mechanism. And in mechanical engineering robotics and biomechanics to describe the motion of systems composed of joined parts such as an engine a robotic arm or the skeleton of the human body. It deals with the relative motion between the various parts.
Iii Kinematics and dynamics. Ii Wheel rolling on a flat surface. In particular these drawings must clearly show the following.
Type of relative motion Type of contact Type of mechanical constraint. 1 Each body the number of bodies and the type of body binary ternary etc. 141 Classification of Kinematic Pairs Kinematic pairs may be classified according to the following considerations.
I Kinematic pairs according to nature of contact. 1 b List different types of Kinematic Pair. I Kinematic pairs according to nature of contact.
Briefly explain the types of instantaneous centres. Describe the working of Oldhams coupling with a neat sketch. According to the following consideration Kinematic Pair has been classified into three types.

0 Comments